Speech Project
Enhancing Open-Set Speaker Identification through Rapid Tuning with Speaker Reciprocal Points and Negative Samples
Overview
We introduces a novel framework for open-set speaker identification in household environments, playing a crucial role in facilitating seamless human-computer interactions. Addressing the limitations of current speaker models and classification approaches, our work integrates an AudioLM frontend with a few-shot rapid tuning neural network (NN) backend for enrollment, employing task-optimized Speaker Reciprocal Points Learning (SRPL) to enhance discrimination across multiple target speakers. Furthermore, we propose an enhanced version of SRPL (SRPL+), which incorporates negative sample learning with both speech-synthesized and real negative samples to significantly improve open-set SID accuracy. Our approach is thoroughly evaluated across various multi-language datasets, demonstrating its effectiveness in achieving high usability for complex household multi-speaker scenarios and significantly enhancing open-set performance.
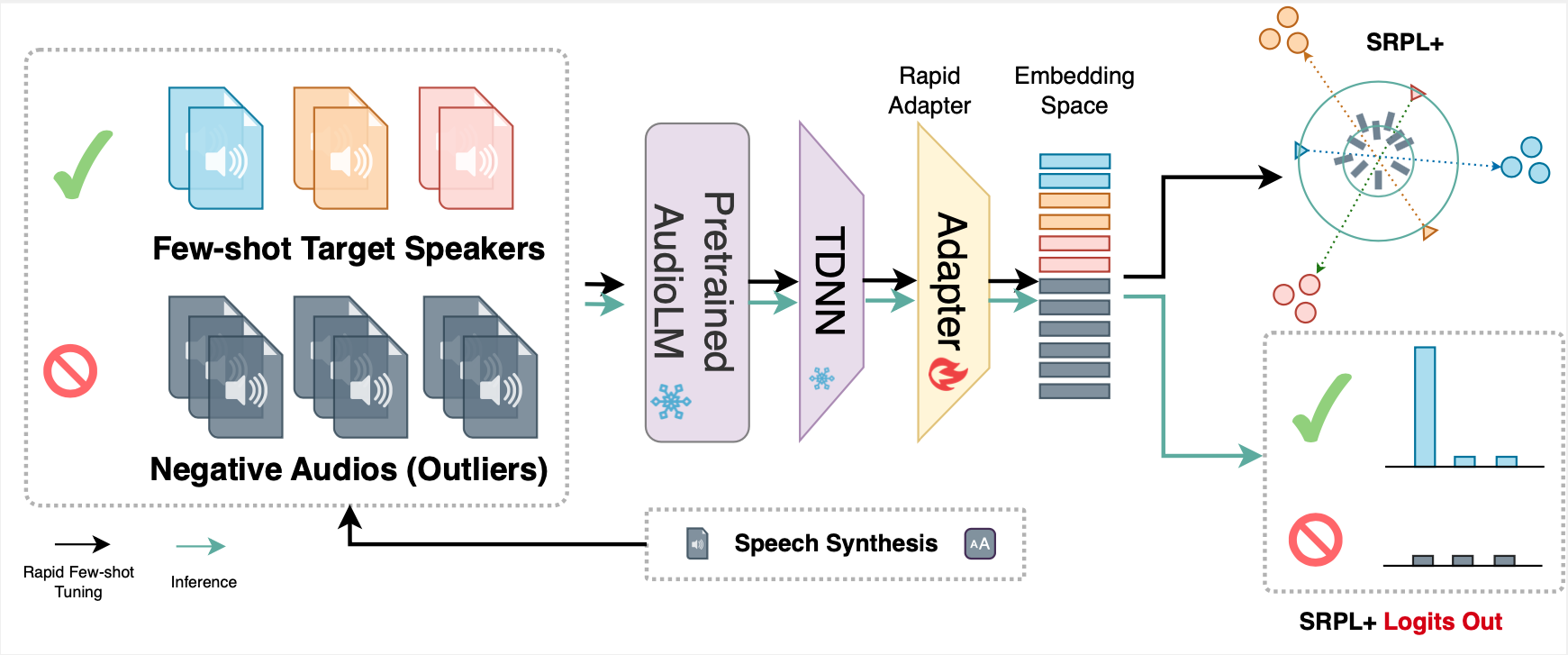
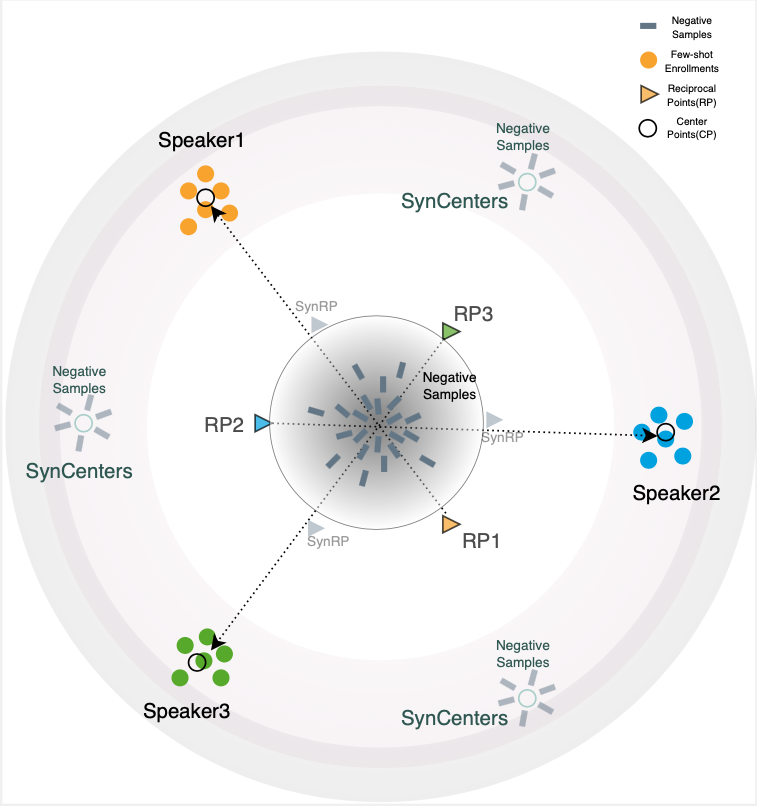
Dataset
We utilize two primary datasets in our research:
Qualcomm Speech: Dataset links and our experimental settings.
Link to Qualcomm Speech dataset
| Target Speakers | Unknown Speakers | N-fold |
|---|---|---|
| 5/10 | 10 | 3 |
FFSVC HiMia: Dataset links and our experimental settings.
| Target Speakers | Unknown Speakers | N-fold |
|---|---|---|
| 5/10 | 10 | 3 |
Example split for training and testing:
Pretrained Audio Large Model
Our methodology is built upon a pretrained audio large model WavLM-base-plus for TDNN speaker verification, specifically designed to capture the nuances of human speech and speaker characteristics. This model serves as the foundation for our rapid tuning process, allowing for effective speaker identification. We use the 512 dimensional WavLM-base-plus with TDNN extracted speaker embedding for our backend rapid tuning and enrollment (SRPL+) models.
Link and Details to the pretrained WavLM-TDNN AudioLM
Evaluations
The evaluation section details the performance metrics on open-set speaker identification. The Open Set Classification Rate (OSCR) calculates the area under the curve mapping the Correct Classification Rate (CCR) for known classes to the False Positive Rate (FPR) for unknown data, offering a threshold-independent evaluation for open-set.

We provide the implementation of core evaluation metrics, along with other evaluation metrics, in our code repository. An inference script is also provided to evaluate the model on our example testing split data.
Inference script and evaluation metrics implementation
Code
Code used in this research for model training, and evaluation, is available for public use after publication. This encourages reproducibility and further experimentation in the field.
Please note: The models, saved checkpoints, and evaluation code for reproducing results are now available. However, the training code for SRPL+ will be released after the publication of our research paper.
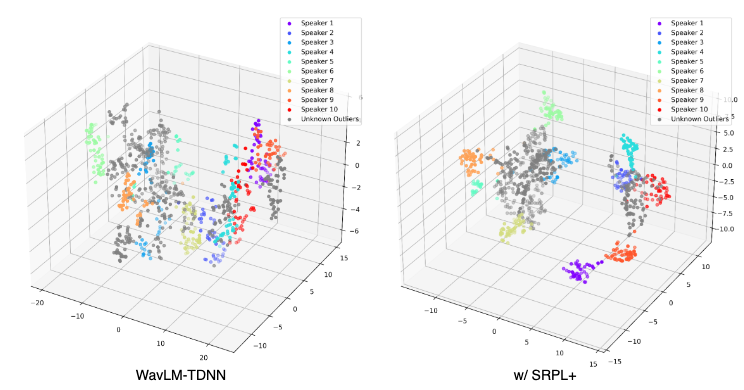
Visualization and Evaluations
We present a series of visualizations and detailed evaluations to illustrate our method’s effectiveness as in the paper. The t-sne embedding plots clearly demostrate the effectiveness of our method.
Citation
Please cite our work if it contributes to your research:
@article{srplplus2024, title={Enhancing Open-Set Speaker Identification through Rapid Tuning with Speaker Reciprocal Points and Negative Samples}, author={Anonymous Authors}, journal={Anonymous Journal}, year={2024}, publisher={Anonymous Publisher} }